Power cables are vital in our daily lives. They connect various devices and ensure that electricity flows efficiently. Dr. Emily Chen, a renowned expert in electrical engineering, once stated, "Without power cables, our technology-driven world would come to a halt." This highlights the essential role these cables play.
Power cables are designed to transmit electrical power from one point to another. They consist of conductors, insulators, and protective covers. The materials used vary based on their application. Often, cables are buried underground or mounted overhead, creating a complex web of connections. Despite their importance, many people overlook their role in our infrastructure.
Not all power cables are created equal. There are differences in voltage ratings and insulation materials. It’s crucial to select the right type for specific needs. However, mistakes can happen, leading to potential hazards. Poor installation or inappropriate usage can result in failures. Constant innovation is necessary to improve safety and performance in this field. The evolution of power cables remains an area needing ongoing attention and reflection.

Power cables are essential for transmitting electricity from one point to another. They connect power sources to devices, enabling them to function correctly. A power cable typically consists of three key components: the conductor, insulation, and protective sheathing. The conductor, usually made of copper or aluminum, carries the electrical current. Insulation surrounds the conductor, preventing short circuits. The outer sheathing protects everything from physical damage.
When working with power cables, consider these tips. Always check the cable specifications before use. Look for the appropriate voltage and current ratings. Using an incorrect cable can lead to overheating and damage. Also, ensure cables are not frayed or exposed. Damaged cables pose serious safety risks.
Another important aspect is proper installation. Cables should be installed according to guidelines. Taking shortcuts can lead to failures or hazards. Pay close attention to the environment where cables are placed. Heat and moisture can significantly affect performance. Regularly inspect cables for wear and tear. Ultimately, care ensures efficiency and safety.
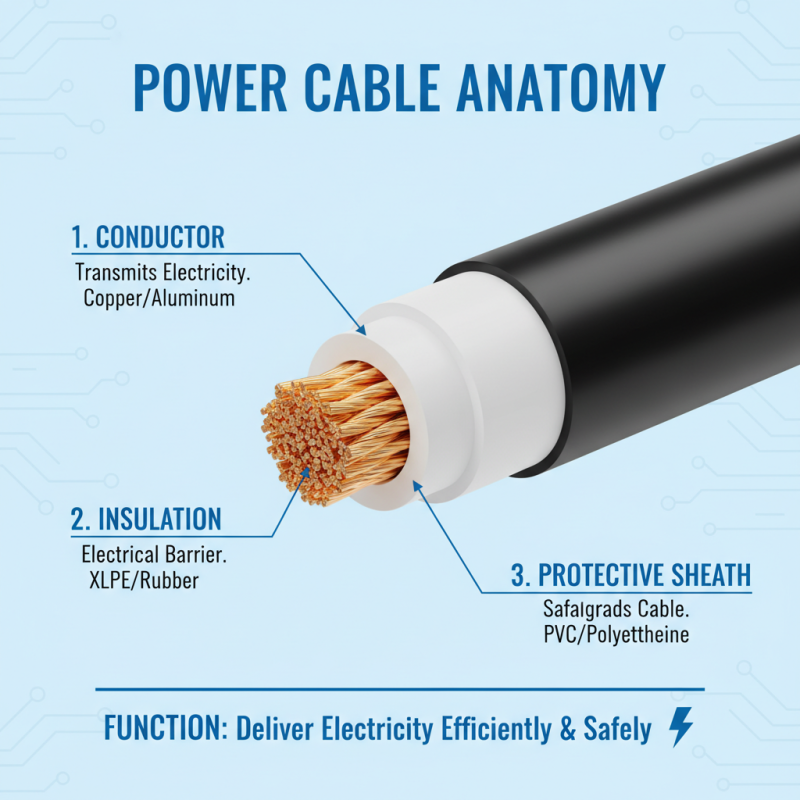
Power cables play a crucial role in delivering electricity. Their construction involves specific materials and structure to ensure efficiency and safety. A typical power cable consists of three main components: the conductor, insulation, and protective sheath.
The conductor is usually made of copper or aluminum. It carries the electric current. Copper, being a better conductor, is more widely used. However, aluminum is lighter and cheaper. The insulation surrounds the conductor. It keeps the current contained. This layer is made from materials like PVC or rubber. These materials protect against electrical shocks and environmental damage.
The protective sheath covers the entire cable. It adds an extra layer of defense against physical damage. It should be durable and resistant to heat and moisture. Over time, wear and tear can occur. Inspecting cables regularly is essential. Issues like fraying or cracking can be dangerous. Identifying these problems early can prevent accidents. Understanding the components of power cables can help in recognizing their importance in our daily lives.
Power cables are essential for the delivery of electricity. They work by allowing electrical flow from one point to another. The basic concept involves conducting electricity through conductive materials, typically copper or aluminum. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), conducted electrical energy can reach high levels, often above 1000 volts in industrial applications.
Electricity flows through circuits, driven by the difference in voltage. The power cable's insulation contains the electrical current. This insulation prevents unwanted contact and reduces the risk of electrical shock. Interestingly, poorly insulated cables can lead to energy loss. Reports show that up to 30% of energy can be lost due to inadequate insulation.
The construction of power cables is also crucial. Many cables contain multiple strands of wire to enhance flexibility. However, not all installations consider the necessary load requirements. A failure to match cable capacity with application loads can lead to overheating and eventual failure. These issues highlight the need for better standards and practices in cable selection.
Power cables are essential for transmitting electricity safely and efficiently. Various types serve distinct purposes. Low voltage cables are common in residential applications. They often range from 0.6kV to 1kV. These cables typically connect houses to the main power grid.
Medium voltage cables fill the gap between low and high voltage applications. They operate in the 1kV to 35kV range. This category is crucial for industrial setups. A report by the International Energy Agency notes that medium voltage systems account for a significant portion of energy loss. High voltage cables, above 35kV, are used for long-distance transmission. These cables are robust and often insulated with materials that withstand harsh conditions.
Despite technological advances, issues remain. Many older installations still rely on outdated cable types. Aging infrastructure poses risks, including voltage drops and cable failures. Regular maintenance and assessments are paramount. The future looks toward improving cable materials and designs. Better insulation and lower energy losses are goals for the industry. This evolution will enhance the reliability of power transmission systems.
This chart illustrates the various types of power cables and their respective applications as a percentage of overall use. Low voltage cables are the most commonly used, followed by medium and high voltage cables, while fiber optic and control cables represent a smaller share of the market.
Power cables are essential in transmitting electricity. However, safety should always come first when using them. Many users overlook critical safety standards. Not following these standards can lead to severe accidents.
It’s crucial to select the right type of power cable for your environment. For instance, outdoor cables must withstand weather conditions. Indoor cables, on the other hand, should be less robust. Yet, people often mix these up. Doing so can present risks like overheating or electrical fires.
Inspection and maintenance are vital. Regular checks can prevent failures. Users should look for signs of wear, such as frayed insulation. Neglecting these details can result in unexpected outages. Some might think they can skip this step. But everything connected to power has risks that are too serious to ignore.